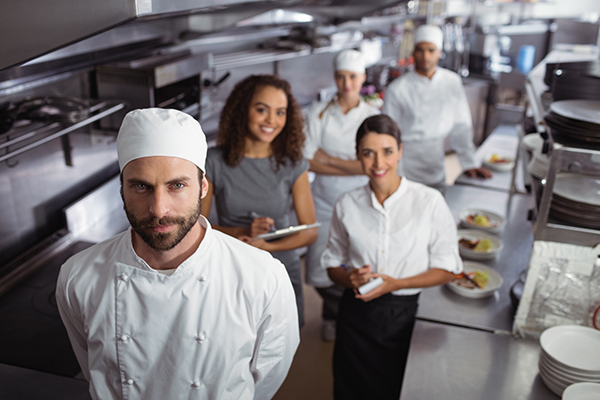
FDA has released the newest version of the Food Code
Blog by Lori Stephens based on the new FDA Food Code release.
The FDA has released an updated version of the federal Food Code – Food Code 2017.
What is the Food Code?
The Food Code is a set of requirements based on science for preparing and serving food.
The Food Code documents the best ways to prevent foodborne illness and injury. It provides guidance for restaurants, retail food stores, vending operations and food service operations, including those in schools, hospitals, nursing homes and child care centers. By following the requirements in the Food Code, these operations can eliminate the most important factors that can cause food safety hazards.
The FDA provides this document to the food industry as a tool. It is a very important fact that the FDA does not require that the Food Code be followed by local health departments and similar organizations – they describe it as “model regulation”. It can be adopted fully, or parts can be used. The FDA allow alternative requirements that offer an equivalent level of food safety.
Why the Food Code important is Important to You
This is important to our business because this document prescribes the use of single-use gloves for handling ready-to-eat food. It is the main regulatory reason restaurants and food service operations use gloves.
A ton of work goes into revising the Food Code
The FDA writes the food code with input from regulatory officials (USDA and CDC), industry, academia, and consumers at an industry meeting of the Conference for Food Protection (CFP).
The Food Code used to be updated and published every two years, the process to develop a Food Code revision is really time consuming. Due to the amount of input, edits, and science involved, the document is now revised every four years.
The effort to create this new revision started in mid-2106 and the document was just published last week. It is called the Food Code 2017 because the contents were agreed on in 2017, even though it was published in 2018. The last revision is called Food Code 2013.
What has changed in the Food Code 2017?
According to the FDA’s statement, significant changes to the Food Code 2017 include:
- Revised requirement for the “Person in Charge” to be a Certified Food Protection Manager
- New section addressing the use of bandages, finger cots or finger stalls
- Harmonized cooking times and temperatures for meat and poultry to ensure uniformity with guidance from the USDA
- Updated procedures during an extended water or electrical outage
If you want to read the Code, or share it with one of your customers, it is available on the FDA website at http://www.fda.gov/FoodCode.