Meat Color and Doneness: Persistent Pinking
Late in June, my family and I were able to visit the Black Hills, an area of the country in which I have not had the opportunity to spend much time. One evening, as we dined at a local restaurant, I observed a table across the dining room sending back a dinner. While I couldn’t hear the entire conversation and I certainly wasn’t trying to eavesdrop, it was apparent that the customer was unhappy with the cooking of their hamburger and was sending it back because it was too pink in the middle. That immediately brought to my mind the phenomenon known as persistent pinking. A term I became familiar with because of work done by some colleagues here at Kansas State, which they present each summer to a group of foodservice operators who join us on-campus for an in-depth week-long look at all things food safety.
Most of us now know that color is not an indicator of doneness for meat products. However, it wasn’t very long ago that even USDA was touting to use meat color as an indicator of doneness. We traditionally find that most foodservice employees know that you can’t use the meat color to know if it has reached the required cooking temperature. When digging into this with employees (and consumers) a bit further, we will often uncover that they believe it could look “cooked” before it reaches the proper endpoint cooking temperature. That is, all signs of pink could be gone from the product, but it may not yet reach the proper temperature. However, many still believe that if it looks pink inside, it is a surefire way to know that it is NOT cooked, but this is not true. I believe this is what was happening that night in the Black Hills when the customer thought his burger was not cooked, when indeed it may well have been.
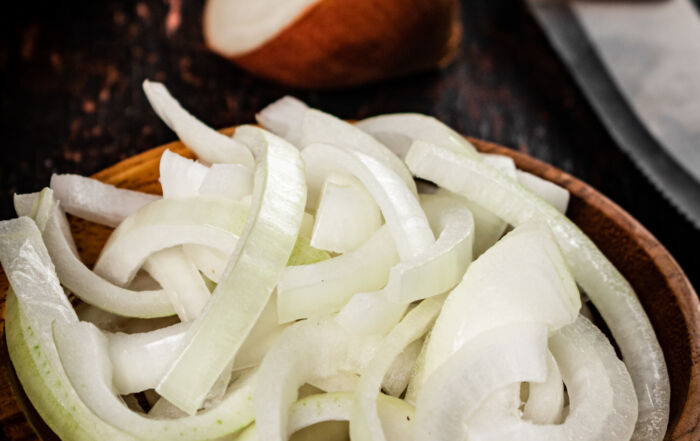
There are instances where meat exhibits persistent pinking, a phenomenon where the meat retains a pink or reddish hue even after thorough cooking.
There are instances where meat exhibits persistent pinking, a phenomenon where the meat retains a pink or reddish hue even after thorough cooking. Persistent pinking is most commonly observed in cooked meat products such as ground beef, sausage, or cured meats. Earlier this summer I had a bratwurst which exhibited the phenomenon. Despite being fully cooked, the meat retained a pink color, which can cause concern among consumers.
There are several factors that contribute to persistent pinking in meat. One of the culprits is the presence of nitrites, commonly used as curing agents in processed meats. Nitrites react with myoglobin to form a stable pink pigment called nitrosomyoglobin, which can persist even after cooking.
Another factor is the pH level of the meat. Higher pH levels, often found in older or mature animals, can contribute to the formation of pink pigments. Additionally, certain bacteria can produce enzymes that interact with myoglobin and contribute to persistent pinking.
Persistent pinking in meat does not necessarily indicate that the meat is undercooked or unsafe to consume. Operators and consumers should rely on additional indicators of meat safety, such as temperature, texture, odor, and storage conditions.
Be sure to purchase meat from reliable sources and verify its freshness. Proper storage at appropriate temperatures (below 40°F) helps maintain the quality and safety of meat products.
Cooking meat to the recommended internal temperatures is crucial. Using a food thermometer to check for doneness is the only way for foodservice operators and employees to ensure that meat reaches a safe temperature throughout.
Persistent pinking in meat can be a puzzling phenomenon. But, by understanding the causes and following proper food safety measures, foodservice operators can ensure the safe consumption of meat.
I’d love to know your thoughts about this – have you experienced persistent pinking and/or had customer complaints about this when you know you’ve safely cooked the product? Reach out to me via email and let me know! Risk nothing,
READ MORE POSTS
What Have We Already Learned from the Most Recent E. Coli Outbreak?
In late-September and peaking in very early-October, reports of increased Escherichia coli (E. coli) 0157:H7 cases [...]
Ensuring Food Safety in Emergency Foodservice Operations
As we were reminded earlier this month, emergencies can strike unexpectedly, whether due to natural disasters, [...]
Ensuring Food Safety in Emergency Foodservice Operations
Last week, many of us across the United States watched in disbelief as the southeastern portion [...]
Despite Gallup Polls, the US Does Have the Safest Food Supply in the World
As I settled into work one morning last week, a headline popped up on my computer [...]