Routes of Foodborne Illness & Germs
 From your sniffling coworker to the raw chicken on your kitchen cutting board, everyday life is full of potential infectious hazards. With germs so common and seemingly everywhere, knowing how germs spread is vital to preventing infection and foodborne illness. There are seven possible ways for the transmission of bacteria and viruses to take place. Although some of these microorganisms in our environment are good for us and protect us, disease causing pathogens are the germs or bad guys.
From your sniffling coworker to the raw chicken on your kitchen cutting board, everyday life is full of potential infectious hazards. With germs so common and seemingly everywhere, knowing how germs spread is vital to preventing infection and foodborne illness. There are seven possible ways for the transmission of bacteria and viruses to take place. Although some of these microorganisms in our environment are good for us and protect us, disease causing pathogens are the germs or bad guys.
In a food service environment, pathogens can be abundant so handwashing, working in your restaurant only when you are healthy, and good sanitation help us limit or shut down these routes of transmission. Some of the routes are not specific to food environments, but helps understand how they all contribute to disease transmission and our efforts for prevention.
Direct Contact –This mode of transmission involves physical contact and generally takes place through shaking hands, touching someone, kissing, sexual contact, etc. Body fluids such as blood, saliva, emesis, or mucous provide the transfer substance. HIV, bloodborne forms of hepatitis, and STD’s would be in this category.
Indirect Contact—Germs are spread between people via an intermediate object, usually something inanimate. Door knobs, railings, counters, tables, and other frequently touched objects are common culprits. Cold viruses and the Norovirus (foodborne illness leader) can be transmitted this way.
Droplet Spread—An infectious agent is spread through the air when two people are near each other (cough, sneeze, or just talking). Respiratory diseases such as influenza are in this category.
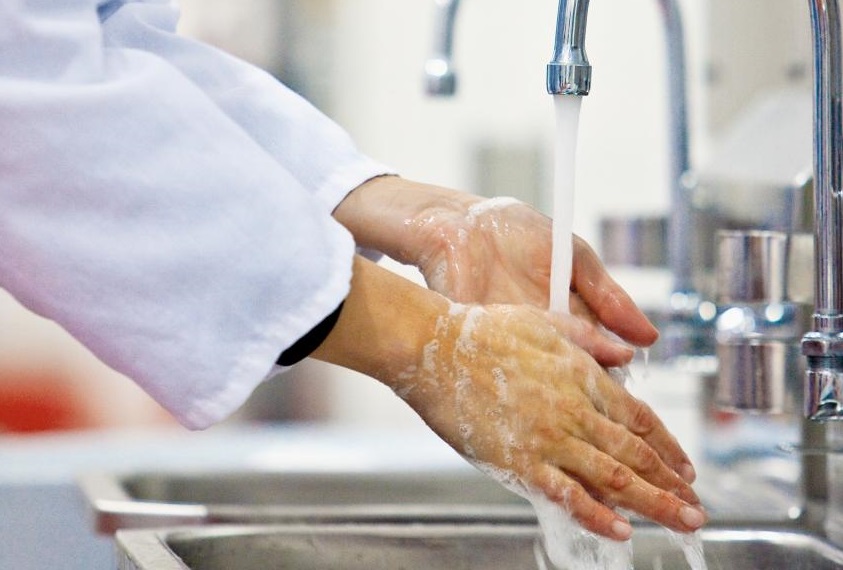
Fecal-To-Oral Route—Here’s our most common foodborne illness route. Transmission occurs when an infected person fails to adequately wash their hands after going to the bathroom and touches food. The person then goes on to have direct contact with another person, such as shaking hands, or spreads germs through indirect contact by contaminating food with hands, for example. If an ill person (viral or bacterial illness) prepares your ready-to-eat food, such as a salad, chances are good you will get that disease. As a little food safety levity, we call this the poopy finger route. Hepatitis A, Norovirus, Salmonella, E. coli, etc. are spread this way.
Common-vehicle Spread—This form of transmission involves a contaminated, inanimate “vehicle” that spreads germs to several or many people. Examples include a city water supply that’s contaminated with parasites or packaged foods tainted with Salmonella or Listeria. Temperature often plays a role in this type of spread since many germs will produce larger amounts of toxin in a warmer, more humid environment, but are kept in check at refrigerated conditions.
Airborne Spread—Germs are spread through the air over a distance of several feet. The infectious organisms are usually contained in tiny droplets that can remain suspended in air for hours or days. Tuberculosis, anthrax, and Norovirus can be spread by airborne transmission. Airborne spread can be affected by the speed of direction of airflow—enclosed spaces with poor air circulation (cruise ships, casinos, airplanes, etc.) can be particularly bad.
Vector-borne Spread—This route is less associated with food. It involves the transfer of germs to a person via the body of another organism (contaminated flies, ticks, or a mosquito from the contact or a bite).
Bottom Line: We continually need to stress to food workers the importance of good personal hygiene, frequent handwashing, using barriers between hands and food, and not taking the risk of working with food when ill or directly exposed to someone who is sick. People preparing our food do literally have a hand in food safety. Understanding the simplicity of disease transmission might have some shock value when training your crew about food safety, so use every tool to help them understand the how, when, why to safer food and a healthy crew.
***
About the Author: Lacie Thrall

This information is provided as a general guideline and is not intended to be, nor does it, constitute legal or regulatory advice. Additional Federal regulations may apply to your particular circumstances. State, regional and local laws, ordinances and regulations may also apply.
READ MORE POSTS
Maintaining your Equipment: Is it the Missing Ingredient in your Recipe for Food Safety?
Although I am no longer in day-to-day operations, between our students and foodservice lab at the university and my volunteer activities in my local church, I keep a close hand in food production. This past week, I had the opportunity to lead a group of men at our church in preparation of a luncheon for 100 women who were attending a spirituality retreat. Over the course of the morning, I realized our main cooler in the kitchen was not functioning properly and was about 10˚F above the required temperature. While we do have a commercial kitchen, we do not routinely log temperatures, so when the unit started to malfunction is questionable. Even more concerning was not the lunch we were preparing for, but the dinner that was served the night before for 300+ families in the parish.
Contamination of Food: Let’s Get Physical
Earlier this month, we began a discussion about contamination of food. Our first blog focused on chemical contamination, but in this blog, I’d like to look at physical contamination of food.
Contamination of Food: Chemicals, Pesticides, and more, Oh My!
If you have followed our blogs, you have often heard us opine about food safety-related behavior and communication, food traceability, and other overarching food safety topics. We often don’t get into the weeds and discuss topics you may have learned about in your food safety training. But I thought we might circle back around and dig into a few of these topics for a few blogs. This month, I’d like to discuss food contamination, this blog will focus on chemical contamination of food and later this month, we will discuss physical contaminates.