Food Traceability in Foodservice Operations: An Essential, and Soon-to-be Required, Component of your Food Safety Plan
In June, I discussed the importance of having a solid food defense plan, and I provided you some resources for developing or strengthening your food defense plan. As I was writing those blogs, my mind kept turning toward food traceability. While they are distinctly different concepts, food traceability goes hand-in-hand with a food defense program. I would argue for your food defense plan to be effective, you must have an effective internal food traceability program, where you can trace the product back to the supplier (backward traceability), but also be able to trace the product from the supplier to the guest who was served the product (forward traceability).
Forward traceability is often the most difficult for foodservice operators. If you are a commercial restaurant operator, this can be extremely difficult if the guest pays with cash, where you have no records to track who dined in your establishment, let alone what food they may have consumed. In schools and other on-site feeding establishments, it can be made difficult due to the sheer number of guests/students fed daily. You might be able to track who dined in your operation on a particular day, but it generally gets a bit more complicated when you try to answer the question of which guests had a certain product from a particular case or lot number.
For several years, the U.S. food supply was only required to have a one-step forward and one-step back traceability. This meant you had to know where your product came from and where it went once it left your operation. The Food Safety Modernization Act provided the groundwork for the Food and Drug Administration to designate foods for which additional record keeping is required to protect the public health. The New Smarter Era of Food Safety Blueprint, laid out by the Food and Drug Administration included improved traceability as one of the four key elements, along with smarter tools and approaches for prevention and outbreak response, new business models and retail modernization, and food safety culture. These four elements serve as the building blocks for a more digital, traceable food system.
If you think that the changes to traceability will not impact your foodservice operation, think again. While it could still change, I would expect some changes to be coming to the traceability landscape for foodservice operations in the coming years.
If you think that the changes to traceability will not impact your foodservice operation, think again. While it could still change, the proposed rule provides only a few exemptions for foodservice operations. Two of the exceptions require the foodservice operation to have 10 or fewer full-time equivalent employees. Another partial exception is in place for schools who participate in farm-to-school programs under the guidance of USDA, but the rule would require them to maintain records of where the product was sourced for a minimum of 180 days.
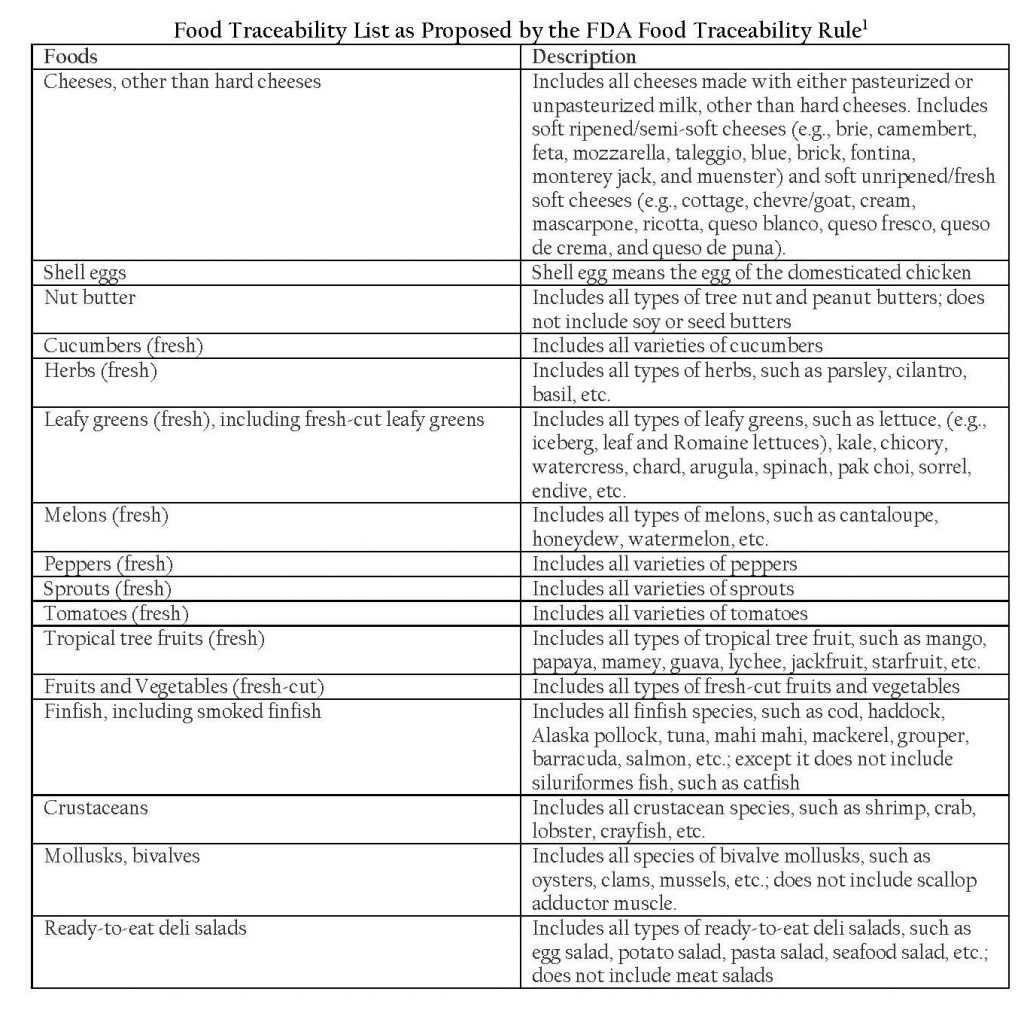
Fundamentally, the proposed rule would require those who manufacture, process, pack, or hold food on a designated food traceability list to establish record keeping data of key elements associated with various Critical Tracking Events. Foods currently on the list are included in the table below.
The end goal of the Food and Drug Administration is to improve the tracking of food to enable end-to-end traceability. To achieve this, records for food product will need to be linked. If a foodborne illness outbreak were to occur, the foodservice operation would be required to provide traceability records in the form of an electronic, sortable spreadsheet to the Food and Drug Administration within 24 hours.
While the proposed changes are currently just that – proposed, I would expect some changes to be coming to the traceability landscape for foodservice operations in the coming years. If the proposed rule is accepted, it would become effective 60 days after publication in the Federal Register. Compliance date for the food industry would be two years after that date.
If you would like to learn more about food traceability, why it is important, how some foodservice operations have embraced traceability, and some tips on getting started – join us for our July SafeBites webinar where I will be presenting more information on Traceability. It is scheduled for July 21 at 1:00 pm. We would love for you to join us.
I hope you have a great 4th of July weekend. Be safe as you travel and enjoy family and friends. Risk Nothing.
[1] Source: Food & Drug Administration. (2021, July 1). FSMA Proposed Rule for Food Traceability. Food Traceability List. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/food/food-safety-modernization-act-fsma/fsma-proposed-rule-food-traceability
READ MORE POSTS
Navigating the Latest Listeria Outbreak…again
Welcome to Food Safety Education Month! Late last month in my blog we talked about this [...]
Score Big in Food Safety: Amp Up Your Food Safety Education Month
It is mid-August and in just a few short weeks it will be that time of [...]
Temperature Checks: Safeguarding Your Foodservice Business with Every Delivery
There is no mistake that for those of us in the Midwest, and much of the [...]
The Critical Role of Staff Training and Education in Food Safety for Foodservice Professionals
In mid-June, my colleagues and I at Kansas State University offered our Serving up Science: The [...]